Coloring Activities and Learning Outcomes

Coloring pictures food groups – Coloring activities offer a fun and engaging way to introduce children to the concept of food groups, transforming a potentially dry subject into a vibrant and memorable experience. The act of coloring itself fosters creativity and fine motor skill development, while the thematic focus on food groups provides a valuable learning opportunity. By associating specific colors and images with different food groups, children can build a stronger understanding of healthy eating habits.Coloring pictures can significantly enhance memory retention of food group information.
The process engages multiple senses and learning styles, creating a multi-sensory experience that strengthens neural pathways and improves recall. Unlike passively reading about food groups, coloring actively involves the child, making the information more meaningful and easier to remember. The visual association created through coloring helps to cement the knowledge in long-term memory.
Creative Coloring Activities for Food Group Education
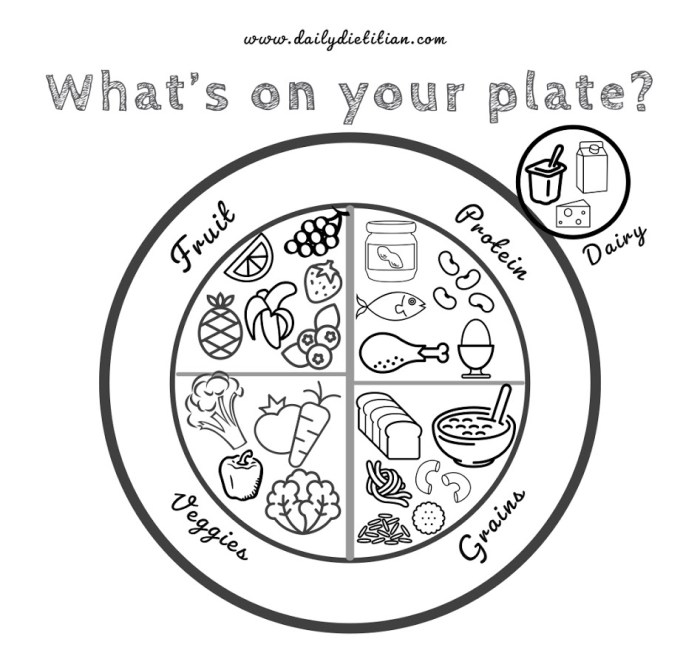
Several creative coloring activities can effectively teach children about food groups. For instance, a worksheet could feature Artikels of various fruits and vegetables, each belonging to a different food group. Children can color them according to their respective groups (e.g., oranges for citrus fruits, greens for leafy vegetables). Another engaging activity involves creating a “MyPlate” coloring page, where children color in different sections of the plate with foods from each food group, promoting portion control awareness.
Finally, a more advanced activity could involve designing their own healthy meal using food group cutouts, requiring them to identify and categorize different food items. These activities transform passive learning into active participation, enhancing comprehension and retention.
The Role of Coloring in Memory Retention
The act of coloring strengthens memory retention through several mechanisms. Firstly, the visual association between the colored image and the food group name creates a strong mnemonic device. Secondly, the fine motor skills involved in coloring stimulate brain activity, improving focus and concentration, which are crucial for learning. Thirdly, the enjoyable nature of coloring enhances engagement and motivation, making the learning process more effective.
Studies have shown that multi-sensory learning, like coloring, is more effective than passive learning methods, leading to better long-term retention of information. For example, a study published in the Journal of Educational Psychology demonstrated that students who engaged in hands-on activities, including coloring, showed significantly better recall of factual information compared to students who only read the material.
Creating a Coloring Book Focused on Healthy Eating
Creating a coloring book focused on healthy eating and food groups involves several key steps. First, research and gather information on the different food groups, their nutritional benefits, and examples of foods within each group. Next, design appealing and age-appropriate illustrations of various foods, ensuring accurate representation and vibrant colors. The illustrations should be simple enough for young children to color easily but detailed enough to be engaging.
Then, incorporate educational text, perhaps short descriptions or fun facts about each food group, alongside the illustrations. Finally, assemble the pages into a book format, ensuring high-quality printing to maintain the vibrancy of the colors. This structured approach ensures the creation of a comprehensive and effective educational tool.
The vibrant hues of the food groups leapt from the page as I colored, a joyful explosion of oranges, greens, and reds. My enthusiasm, however, quickly turned to dismay as my hands became a kaleidoscope of color themselves! Thankfully, I found a helpful guide on how to remove food coloring from hands , and soon my fingers were clean, ready to continue my artistic exploration of healthy eating.
Advanced Coloring Techniques and Food Representation: Coloring Pictures Food Groups
Coloring isn’t just about filling in shapes; it’s a powerful tool for teaching children about the world, especially the fascinating world of food. By employing advanced coloring techniques, we can elevate these activities from simple exercises to engaging explorations of texture, color, and the visual appeal of different food groups. This allows children to develop a deeper understanding and appreciation for healthy eating.The key lies in understanding how different shading and coloring techniques can mimic the diverse appearances of various foods.
Imagine the smooth, glossy surface of a ripe strawberry versus the rough, textured skin of an orange. These visual differences can be beautifully captured through the strategic application of color and shading. Similarly, the vibrant hues of fruits and vegetables, and the more muted tones of grains and proteins, offer a rich palette for exploration and creative expression.
Shading and Blending Techniques for Food Texture
To effectively represent food textures through coloring, children can experiment with various shading and blending techniques. For example, a light, gradual shading can create the illusion of a smooth, curved surface like that of a grape or an apple. Conversely, short, quick strokes of color, perhaps using different shades of the same color, can effectively represent a rougher texture, like that of a potato or a piece of broccoli.
Blending colors, using techniques like layering or stippling, allows for a more realistic depiction of the subtle color variations found in many foods. For instance, a ripe mango might be rendered using a blend of yellows, oranges, and reds, gradually transitioning from one hue to the next. The contrast between light and shadow can also be used to add depth and realism.
Consider a slice of bread; the areas facing the light would be lighter in color, while the shadowed parts would be darker, creating a three-dimensional effect.
Visual Comparison of Food Groups Through Coloring, Coloring pictures food groups
Comparing and contrasting the visual representation of different food groups through coloring provides a valuable learning opportunity. Children can explore the diverse colors and textures associated with each group. For example, the bright, varied colors of the fruit and vegetable group contrast sharply with the more earthy tones of the grains group. The coloring process itself encourages children to observe and analyze these differences, strengthening their visual perception and understanding of the nutritional diversity within each food group.
A direct comparison of a brightly colored bell pepper against a slice of whole-wheat bread vividly illustrates the differences in texture and color. This visual learning reinforces the concept that a balanced diet includes a variety of colors and textures.
Tips for Teaching Children About Food Groups Using Coloring Activities
Effective teaching requires a strategic approach. Here are some crucial tips to maximize the educational value of coloring activities focused on food groups:
Using coloring activities to teach about food groups offers a unique blend of fun and learning. By focusing on visual representation and encouraging creative exploration, children develop a deeper understanding and appreciation for healthy eating habits.
- Start with simple shapes and colors: Begin with basic representations of fruits and vegetables, gradually introducing more complex shapes and colors as children develop their skills.
- Encourage experimentation with different media: Crayons, colored pencils, watercolors—each medium offers unique opportunities for exploring texture and color.
- Incorporate real-life examples: Use real fruits and vegetables as references, encouraging children to observe their shapes, colors, and textures firsthand.
- Make it interactive: Engage children in discussions about the different food groups, their nutritional benefits, and their visual characteristics.
- Relate coloring to healthy eating habits: Discuss the importance of a balanced diet, emphasizing the need for variety within each food group.
Questions and Answers
What age group are these coloring pages suitable for?
These coloring pages are adaptable for preschoolers through early elementary school, adjusting complexity based on the child’s developmental stage.
Can I use these coloring pages for classroom instruction?
Absolutely! These pages are perfect for classroom use, offering a hands-on learning experience that complements existing curriculum.
Where can I find printable versions of the coloring pages?
Printable versions will be available [link to download or website].
Are there different difficulty levels available?
While not explicitly tiered, simpler designs can be adapted for younger children, while more intricate designs challenge older children.



